In the digital age, the landscape of commerce has undergone a significant evolution with the emergence of e-commerce. This shift has not only revolutionized the way businesses operate but has also left a profound impact on society, the economy, and emerging markets worldwide. Let’s delve into the multifaceted effects of e-commerce on various facets of business.
Opportunities of E-Commerce on Business
For businesses, e-commerce presents a myriad of opportunities for growth and expansion. It offers a cost-effective platform to reach a global audience, bypassing the barriers of traditional retail channels. Furthermore, e-commerce allows for personalized marketing strategies, tailored to individual consumer preferences and behavior. Additionally, the scalability of e-commerce enables businesses to adapt quickly to changing market dynamics and consumer demands.
What is the Impact of E-Commerce on Business
The impact of e-commerce on businesses is profound, enabling them to expand their reach, improve efficiency, and foster innovation in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
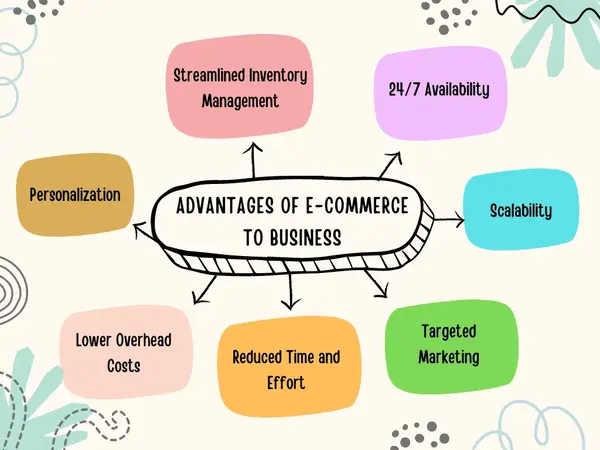
1. Increased Market Reach
Here are the key points on how e-commerce breaks down geographical barriers:
- Global Market Access: Businesses can sell to customers worldwide, transcending physical location limitations.
- Increased Customer Reach: E-commerce allows businesses to reach customers across regions, countries, and even continents.
- Growth and Revenue Opportunities: This expanded market opens doors for significant business growth and revenue generation.
2. 24/7 Availability
Here are the key points on the benefits of 24/7 availability in e-commerce:
- Convenience for Customers: Customers can shop anytime, anywhere, according to their own schedules.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: This flexibility and ease of access lead to a more satisfying shopping experience.
- Increased Sales Potential: Businesses can capture impulse purchases and cater to a global audience with different time zones.
3. Cost Efficiency
E-commerce offers significant cost advantages over traditional retail:
- Reduced overhead costs: Businesses save on expenses like rent, utilities, and staffing for physical stores.
- Scalable pricing models: E-commerce platforms often charge based on usage, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they need (e.g., storage space, bandwidth).
- Improved profit margins: These factors lead to lower overall business costs, which can translate to higher profit margins.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
- E-commerce = Big Data: E-commerce platforms collect a massive amount of data on customer behavior, including what they buy, how they browse, and their preferences.
- Data Analytics = Business Insights: Businesses can use analytics tools to analyze this data and gain valuable insights about their customers, market trends, and how well their products are performing.
- Marketing Optimization: They can use data to improve their marketing strategies, targeting the right people with the right message at the right time.
- Meeting Customer Needs: Ultimately, this data-driven approach allows businesses to tailor their offerings to what customers truly want and need.
5. Improved Customer Engagement
Here are the key points on how e-commerce platforms boost customer engagement and interaction:
- Enhanced Engagement: E-commerce platforms offer features like personalized recommendations and targeted promotions to keep customers interested.
- Interactive Shopping: Interactive features can be used to create a more engaging shopping experience, fostering stronger connections with customers.
- Building Brand Loyalty: By personalizing the shopping experience and fostering interaction, businesses can build brand loyalty.
- Gathering Customer Feedback: E-commerce platforms allow businesses to easily collect reviews and feedback from customers.
- Continuous Improvement: This feedback can be used to improve products, services, and the overall customer experience, leading to innovation.
6. Streamlined Operations
Here are the key points on how e-commerce streamlines business operations:
- Automated Processes: E-commerce automates tasks like inventory tracking, order processing, and shipping, reducing manual work and errors.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation leads to lower labor costs associated with these tasks.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlined operations make businesses run more efficiently overall.
- Integration with Other Systems: E-commerce platforms can connect with accounting, CRM, and other systems, creating a smoother workflow.
- Enhanced Productivity: Automation and integration boost overall business productivity.
7. Diversification of Sales Channels
Here are the key points on how e-commerce helps diversify sales channels:
- Multiple Sales Channels: Businesses can sell beyond their own website using marketplaces, social media, and mobile apps.
- Increased Visibility and Reach: This diversification exposes their products to a wider audience and increases brand awareness.
- Reduced Reliance on a Single Channel: By not relying on one channel, businesses are less vulnerable to disruptions or changes in that channel.
- Enhanced Business Resilience: Diversification strengthens a business’s ability to adapt to market fluctuations.
8. Innovation and Adaptability
Here are the key points on how e-commerce fosters a culture of innovation and adaptability:
- Constant Evolution: E-commerce demands continuous improvement to keep up with customer expectations and technology.
- Innovation Focus: Businesses experiment with new product offerings, marketing strategies, and customer experiences.
- Competitive Advantage: Innovation helps businesses stay ahead of the competition in a fast-paced environment.
- Staying Relevant: Adaptability ensures businesses remain relevant in a constantly evolving marketplace.
Impact of E-Commerce on Emerging Markets
In emerging markets, e-commerce has been a game-changer, providing access to goods and services previously unavailable or unaffordable. E-commerce has a profound impact on emerging markets, bringing about several significant changes and opportunities:

1. Economic Growth
E-commerce facilitates economic growth in emerging markets by creating new business opportunities, generating employment, and stimulating entrepreneurship. It allows small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to access global markets, expand their customer base, and increase sales revenue.
2. Market Access
E-commerce provides businesses in emerging markets with access to a global customer base without the need for physical presence in multiple locations. This expands market opportunities and reduces dependence on local markets, fostering international trade and economic integration.
3. Financial Inclusion
E-commerce contributes to financial inclusion in emerging markets by providing access to digital payment systems, banking services, and credit facilities for individuals and businesses previously underserved by traditional financial institutions. It enables cashless transactions, reduces transaction costs, and promotes financial empowerment among marginalized populations.
4. Rural Development
E-commerce bridges the urban-rural divide by connecting rural entrepreneurs and farmers to national and international markets. It enables them to sell their products directly to consumers, access a wider range of buyers, and obtain fair prices for their goods, thereby improving livelihoods and reducing poverty in rural areas.
Here are the key points on how e-commerce bridges the urban-rural divide:
- Connects Rural Sellers to Wider Markets: E-commerce platforms connect rural entrepreneurs and farmers to national and international markets, bypassing the limitations of local geography.
- Direct Sales to Consumers: Rural producers can sell directly to consumers, reducing reliance on middlemen and potentially increasing profits.
- Improved Rural Livelihoods: By enabling higher incomes from product sales, e-commerce can improve the livelihoods of people in rural areas.
- Reduced Rural Poverty: Increased earning potential through e-commerce sales can contribute to poverty reduction in rural communities.
5. Infrastructure Development
The growth of e-commerce in emerging markets drives investment in digital infrastructure, including internet connectivity, mobile networks, and online payment systems. This improves access to technology and communication services, enhances connectivity, and fosters innovation and economic development.
Here are the key points on how e-commerce growth in emerging markets fuels investment in digital infrastructure:
- Digital Infrastructure Boost: E-commerce growth sparks investment in internet connectivity, mobile networks, and online payment systems.
- Improved Tech Access: This investment increases access to essential technology and communication services for people in these markets.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Better infrastructure leads to overall improved connectivity within the emerging market.
6. Job Creation
E-commerce stimulates job creation in emerging markets by creating employment opportunities in online retail, logistics, digital marketing, web development, and customer support. It enables individuals to work remotely, freelance, or start their own online businesses, providing flexibility and economic independence.
7. Consumer Empowerment
E-commerce empowers consumers in emerging markets with access to a diverse range of products, competitive prices, and convenient shopping experiences. It increases consumer choice, transparency, and purchasing power, enabling consumers to make informed decisions and obtain value for money.
Here are the key points on how e-commerce empowers consumers in emerging markets:
- Greater Product Variety: E-commerce offers access to a wider and more diverse selection of products compared to local stores.
- Competitive Pricing: Online marketplaces often allow for price comparison and potentially lower prices due to increased competition.
- Increased Consumer Choice: E-commerce empowers consumers with more options and the ability to choose products that best suit their needs.
- Transparency in Pricing: Online platforms can provide clearer information on product features and pricing, fostering better purchasing decisions.
- Enhanced Purchasing Power: Potentially lower prices and a wider selection can lead to increased purchasing power for consumers.
8. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Here’s a breakdown of the points on how e-commerce fosters entrepreneurship and innovation in emerging markets:
- Lowered Entry Barriers: E-commerce makes it easier to start a business by reducing costs associated with physical stores, inventory management, and staff.
- Creativity and Risk-Taking: The ease of entry encourages entrepreneurs to be creative with product offerings and take calculated risks in the market.
- Adaptability: The fast-paced nature of e-commerce demands adaptability, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
- Economic Growth: Increased entrepreneurship and innovation drive economic growth and competitiveness within the emerging market.
- Experimentation Platform: E-commerce allows for testing new business models and technologies with a wider audience at a lower cost compared to traditional methods.pen_spark
9. Government Revenue Generation
E-commerce generates tax revenue for governments in emerging markets through value-added taxes, customs duties, and other levies on online transactions. Here are the key points on how e-commerce generates tax revenue for governments in emerging markets:
- Taxation on Online Transactions: E-commerce creates new avenues for governments to collect tax revenue through:
- Value-Added Taxes (VAT): Taxes levied on the difference between the purchase price of a good and the price it was sold for at earlier stages in the supply chain.
- Customs Duties: Taxes applied to imported goods entering the country.
- Other Levies: Additional fees or taxes specific to online transactions.
- Increased Public Finances: These taxes contribute to a larger pool of government revenue.
- Funding for Development: This revenue can be used to invest in crucial areas like:
- Sustainable Development: Increased tax revenue allows for investments that promote long-term economic growth and social well-being.
- Poverty Reduction: By supporting social programs and economic development, e-commerce tax revenue can contribute to poverty reduction efforts.
10. Social Transformation
E-commerce facilitates social and cultural exchange, fosters digital inclusion, and promotes inclusive economic growth in emerging markets. It enables cross-border collaboration, knowledge sharing, and cultural diversity, leading to positive transformations in communities and societies.
Impact of E-Commerce on Economy
The rise of e-commerce has contributed significantly to economic growth.
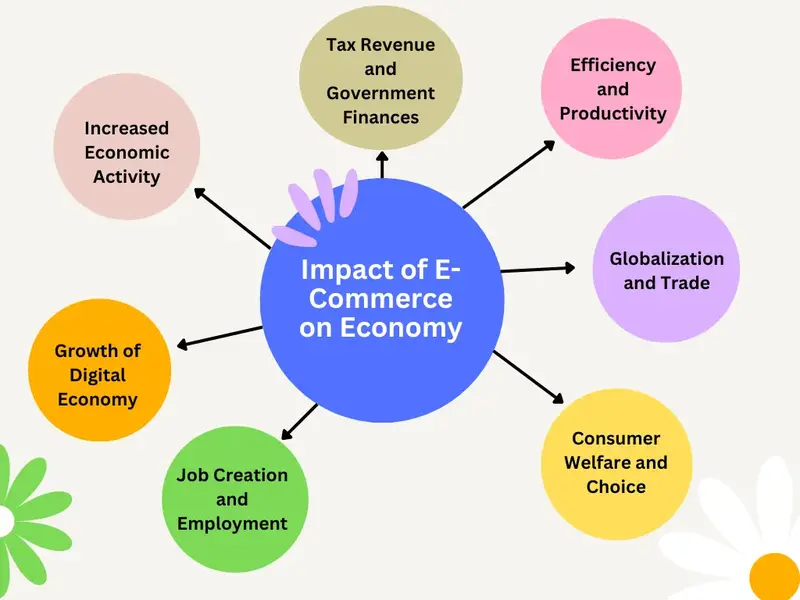
1. Increased Economic Activity
E-commerce stimulates economic activity by facilitating online transactions, creating new business opportunities, and expanding market reach. It drives consumer spending, business investment, and job creation across multiple sectors of the economy.
2. Growth of Digital Economy
E-commerce is a driving force behind the growth of the digital economy, which encompasses online retail, digital services, e-commerce platforms, and related industries. It contributes to GDP growth, productivity gains, and technological innovation, driving economic transformation and competitiveness.
3. Job Creation and Employment
E-commerce generates employment opportunities in online retail, logistics, digital marketing, web development, and customer support. It creates jobs across the entire value chain, from product design and manufacturing to sales and distribution, contributing to labor market expansion and income generation.
4. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
E-commerce fosters entrepreneurship and innovation by lowering barriers to entry, providing access to global markets, and enabling experimentation with new business models and technologies. It encourages creativity, risk-taking, and adaptability, driving economic dynamism and competitiveness.
5. Globalization and Trade
E-commerce facilitates cross-border trade and globalization by connecting businesses and consumers across different countries and regions. It reduces trade barriers, expands market access, and fosters international exchange of goods, services, and ideas, leading to greater economic integration and interdependence.
6. Efficiency and Productivity
E-commerce improves efficiency and productivity in the economy by streamlining supply chains, reducing transaction costs, and increasing the speed and accuracy of transactions. It enables businesses to automate processes, optimize resource allocation, and respond more effectively to market demand, enhancing overall economic performance.
7. Consumer Welfare and Choice
E-commerce benefits consumers by providing access to a wide range of products, services, and price options. It increases consumer choice, convenience, and affordability, empowering consumers to make informed decisions and obtain value for money, leading to higher consumer welfare and satisfaction.
8. Infrastructure Development
The growth of e-commerce drives investment in digital infrastructure, including internet connectivity, mobile networks, and online payment systems. It spurs innovation and upgrades in telecommunications, logistics, and financial services, improving access to technology and communication services, and supporting economic development.
9. Tax Revenue and Government Finances
E-commerce generates tax revenue for governments through value-added taxes, customs duties, and other levies on online transactions. It contributes to public finances, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs, supporting sustainable economic growth and public service provision.
10. Social and Environmental Impacts
E-commerce has social and environmental impacts, including changes in consumer behavior, urbanization, and environmental sustainability. It affects transportation patterns, energy consumption, and waste generation, necessitating policies and practices to mitigate negative externalities and promote responsible e-commerce practices.
Impact of E-Commerce on Society
1. Consumer Convenience
E-commerce provides consumers with unparalleled convenience, allowing them to shop anytime, anywhere, from a wide selection of products and services. This convenience saves time and effort, enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals.
2. Access to Global Markets
E-commerce breaks down geographic barriers, enabling individuals and businesses to access global markets and connect with customers worldwide. This expands economic opportunities, fosters international trade, and promotes cultural exchange and diversity.
3. Social Connectivity
E-commerce platforms facilitate social interaction and connectivity, allowing users to connect, communicate, and share experiences with friends, family, and communities online. This fosters social cohesion, strengthens relationships, and builds virtual communities around shared interests and values.
4. Job Creation and Employment
E-commerce creates job opportunities in various sectors, including online retail, logistics, digital marketing, and customer support. It provides flexible work arrangements such as remote work, freelancing, and gig economy jobs, expanding employment options and income opportunities for individuals.
5. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
E-commerce empowers entrepreneurs and small businesses to launch and grow their ventures, reach a global audience, and innovate with new products, services, and business models. It fosters creativity, risk-taking, and adaptability, driving economic dynamism and competitiveness.
6. Digital Inclusion
E-commerce contributes to digital inclusion by providing opportunities for individuals with limited access to traditional markets or physical stores to participate in economic activities. It reduces barriers to entry for small businesses and entrepreneurs, enabling them to reach customers and compete in the digital economy.
7. Cultural Influence and Diversity
E-commerce influences cultural norms, social behaviors, and consumption patterns by shaping preferences, values, and lifestyles through online advertising, marketing, and product recommendations. It reflects and reinforces cultural trends, societal norms, and consumer aspirations in the digital age.
8. Privacy and Data Security
E-commerce raises concerns about privacy and data security due to the collection, storage, and sharing of personal information and transaction data. It poses risks such as identity theft, fraud, and unauthorized access to sensitive information, necessitating measures to protect user privacy and data security.
9. Urbanization and Environmental Impact
E-commerce contributes to urbanization and changes in consumption patterns, transportation, and logistics, leading to environmental challenges such as traffic congestion, air pollution, and carbon emissions. It underscores the importance of sustainable practices and green initiatives in e-commerce operations and supply chains.
10. Ethical and Social Responsibility
E-commerce platforms have a responsibility to uphold ethical standards and social values, including fair labor practices, responsible sourcing, and environmental sustainability. They play a role in shaping societal norms and expectations around corporate social responsibility and ethical business conduct in the digital age.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the impact of e-commerce on business cannot be overstated. As we’ve explored, the digital marketplace has fundamentally transformed industries, consumer habits, and business strategies. While e-commerce has brought about transformative changes to the business landscape, it is essential to recognize both its opportunities and challenges. By harnessing the power of e-commerce effectively, businesses can unlock new avenues for growth and innovation while addressing the evolving needs and expectations of consumers in the digital age.